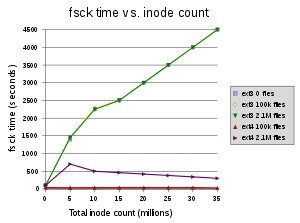
force recheck on reboot – fsck
If you want to force a fsck re-check on reboot, then just
touch /forcefsck
Related articles
Continue reading
If you want to force a fsck re-check on reboot, then just
touch /forcefsck
Continue reading
In my previous post on check filesystem regurlarly, I mentioned tune2fs. That tool give quite a lot of information. But just in case, you did not find what you are looking for in the output, then you can get much more information on these partitions with the dumpe2fs command.
Continue readingIt is always “Better safe than sorry” so, here are some things you
should do..
First check fstab, if you have partitions other than root then use UUID instead of device:
UUID=a8f13a0d-3f1f-42e4-b076-f44b4163306c /mnt/Backup ext4 defaults,relatime 1 2
Then entries for all your mounts should be like above.
Points to note here :
Disk is mounted using the UUID and not with /dev/sdXX. This ensures
that even if your disk ids change, you will be able to mount them. To
get the partition UUID, you can execute :
A nice article here
EncFS is an easy-to-use, command-line tool for storing information in encrypted form. It’s not really a file-system, but it pretends to be one at the CLI. If you’ve been searching for a means of encrypting and decrypting your sensitive data easily, here it is.
User Level: Intermediate
EncFS is included with the distribution I’m using on the desktop, Ubuntu Dapper, so all I needed to do to install it was a few clicks in Synaptic. Look for the encfs package, and select if for installation. It should pull down all of the dependencies for the system. If you’re not so lucky, and your distro doesn’t include EncFS packages, you can download the latest tarball from a here and build it from the source. See the EncFS site for a dependencies.